Absolute pressure – meaning, measurement, and applications
In many technical and scientific fields, precise pressure measurement is essential. Among the different types of pressure measurement, absolute pressure plays a particularly important role. Absolute pressure refers to the pressure measured relative to a perfect vacuum (0 Pa), making it independent of environmental influences such as altitude or weather conditions. This accuracy is crucial in industries where even minimal deviations can affect safety, product quality, or experimental outcomes.
Understanding absolute pressure is therefore essential for engineers, technicians, and researchers across multiple industries. The following sections explain its meaning, measurement principles, formula, applications, and common challenges.
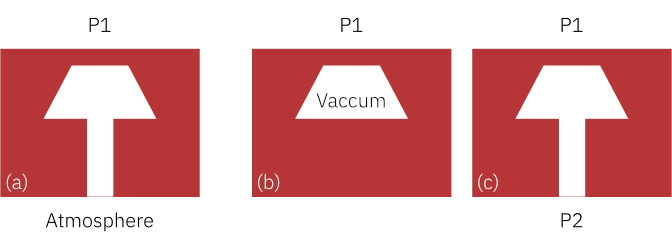
Relative or gauge (a), where the pressure is referenced to the atmosphere
Absolute (b), where the pressure is measured against a reference vacuum sealed inside the chip assembly
Differential (c), where the pressure is measured as the difference between two pressures (delta P or Δ P)
What is absolute pressure?

Absolute pressure is defined as the total pressure exerted on a system, including both the internal pressure and the atmospheric component. Unlike relative pressure, which is referenced to the surrounding atmosphere, absolute pressure always relates to a vacuum reference point. The abbreviation for absolute pressure is typically p_abs, and the SI unit is Pascal (Pa).
For example: if the pressure inside a sealed container is measured at sea level, the value includes both the container’s internal pressure and the surrounding atmospheric pressure. This distinction between pressure and absolute pressure ensures that measurements remain accurate and independent of location or weather conditions.
The formula of absolute pressure
How absolute pressure is measured
The absolute pressure formula expresses the relationship between gauge and atmospheric pressure:
p_abs = p_gauge + p_atm
Where:
- p_abs = absolute pressure
- p_gauge = gauge pressure (relative to ambient air)
- p_atm = atmospheric pressure
This formula of absolute pressure allows engineers to easily convert between different measurement values, provided the local atmospheric pressure is known. This is particularly important in mobile or outdoor applications, where ambient conditions can fluctuate.
Absolute pressure measurement is performed using sensors that contain a sealed reference chamber evacuated to a near-perfect vacuum. The sensor detects the difference between the process pressure and this stable vacuum. Because the vacuum reference remains constant over time, the resulting signal corresponds directly to the true absolute pressure.
High-quality MEMS-based sensors use either piezoresistive or capacitive principles to ensure long-term stability and repeatability. Depending on the application, absolute air pressure sensors can be miniaturised for mobile devices or designed to withstand harsh industrial environments.
Applications of absolute pressure
Absolute pressure is essential in many industries and scientific processes, ensuring accurate, reproducible results. Some of the most important applications include:
Vacuum technology
Absolute pressure measurement is critical in vacuum chambers used for coating processes, semiconductor manufacturing, and laboratory experiments. Only absolute pressure values can ensure a reliable and comparable vacuum environment.
Aerospace and aviation
Aircraft and spacecraft require highly precise absolute air pressure data for altitude calculation, cabin environment monitoring, and airspeed calculation. In space technology, absolute pressure is indispensable, as there is no atmosphere to serve as a reference.


Weather forecasting
Meteorology depends on accurate absolute pressure measurement to predict atmospheric changes and weather conditions. Long-term data sets also provide insights into climate developments.
Industrial processes
From distillation columns to reactors, many processes depend on accurate pressure control. Only absolute pressure values guarantee consistent results, especially in chemical and pharmaceutical production.
Common sources of error in absolute pressure measurement

While modern devices achieve excellent precision, certain factors can influence accuracy:
- Temperature effects: Changes in ambient or process temperature can lead to material expansion or contraction, shifting sensor output.
- Mechanical stress: Mounting methods and vibrations may introduce minor signal deviations.
- Contamination: Dust or moisture can affect the sensor’s diaphragm and stability.
- Calibration drift: Over time, even the best sensors require recalibration to maintain accuracy.
By understanding these challenges, engineers can select the right equipment and implement effective countermeasures.
How temperature affects absolute pressure
Summary and practical relevance
Temperature directly affects gas density and molecular activity, which in turn influences pressure. According to the ideal gas law, when the temperature of a sealed volume increases, the absolute pressure rises proportionally. This effect is especially relevant in environments with strong temperature variations, such as engine testing or environmental chambers.
High-quality sensors often include built-in temperature compensation to minimise these effects and ensure stable, reliable readings.
Absolute pressure is one of the most reliable and universally applicable forms of pressure measurement. Whether in aerospace, medicine, industry, or research, it enables consistent results independent of altitude or weather conditions. Understanding the absolute pressure meaning, the absolute pressure formula, and the principles of absolute pressure measurement is essential for engineers and technicians in demanding applications.

Learn more about abolute pressure sensors
For practical solutions, please visit our product page on pressure sensors or contact us for tailored support.
